Particleworks 8.1
During our conference in Frankfurt, the Particleworks Experience, we hosted Prometech Software, the Japan-based developers of Particleworks. In collaboration with engineers from EnginSoft and Particleworks Europe, we conducted a 1-day workshop showcasing the new features of Particleworks 8.1 and Granuleworks 3.1. The workshop focused on multiphysics simulations involving gas, liquid, and granular materials.

Outline
1. Improved Air Solver (MPS multi phase, FVM Thermal)
- Two-Phase Flow Solver: Particleworks 8.1 introduces a new method for simulating gas-liquid flows using only MPS particles.
- FVM Enhancements: The Finite Volume Method (FVM) solver sees several improvements, including stability enhancements and the addition of a thermal solver.
2. Multi-resolution Capabilities
- Local Refinement: New tools and features allow for better control over resolution in specific areas of the simulation.
- Mapping Advancements: Particleworks 8.1 boasts enhanced mapping capabilities, including new outputs, a default value setting, and a statistics file.
- Custom Grid Interval: Users can now define varying grid intervals for different elements, leading to significant memory savings and more efficient simulations.
3. Multi-Physics and GPU acceleration
- CFD-DEM Interaction: The software's ability to simulate interactions between fluids and particles is bolstered with new features and models.
- Rigid Body Motion: Particleworks 8.1 introduces the capability to simulate 6-DOF rigid body motion, allowing for more complex fluid-structure interaction analyses.
- GPU Computing and Scalability: The software continues to leverage GPU computing power for fast and efficient simulations.
1. Improved Air Solver (MPS multi phase, FVM Thermal)
Advanced Two-Phase Flow Model: The introduction of a two-way coupled two-phase flow model (MPS-MPS) allows for a more realistic simulation of interactions between gas and liquid phases. This advancement enables the analysis of complex scenarios like gearbox lubrication where the influence of air on oil behavior is crucial.
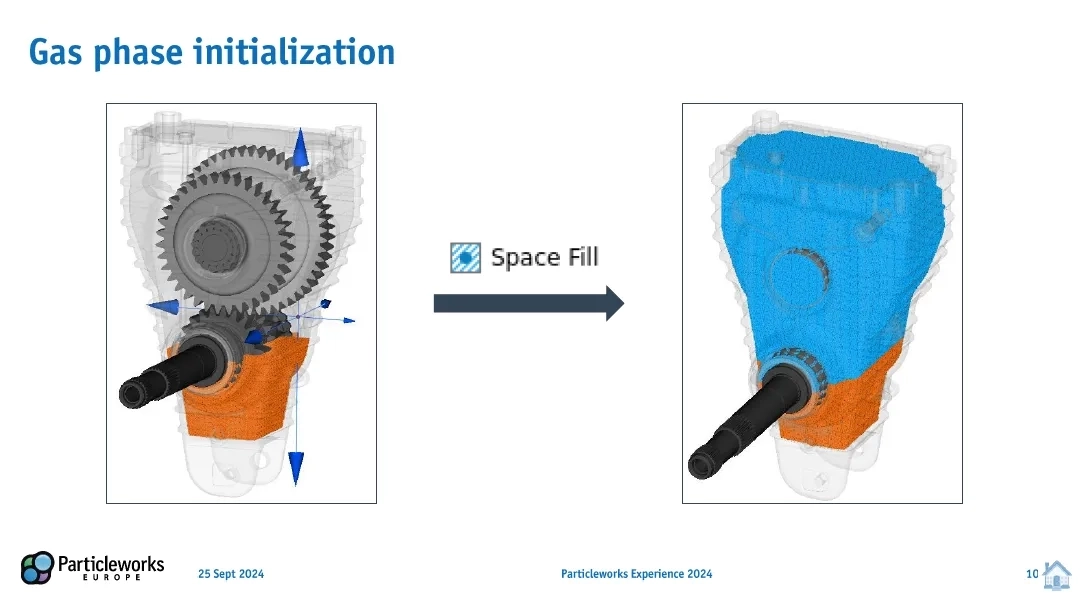
The new Space Fill tool simplifies gas phase initialization by enabling the direct filling of closed volumes with particles. This eliminates the need for filling planes, leading to faster setup, especially for intricate geometries.
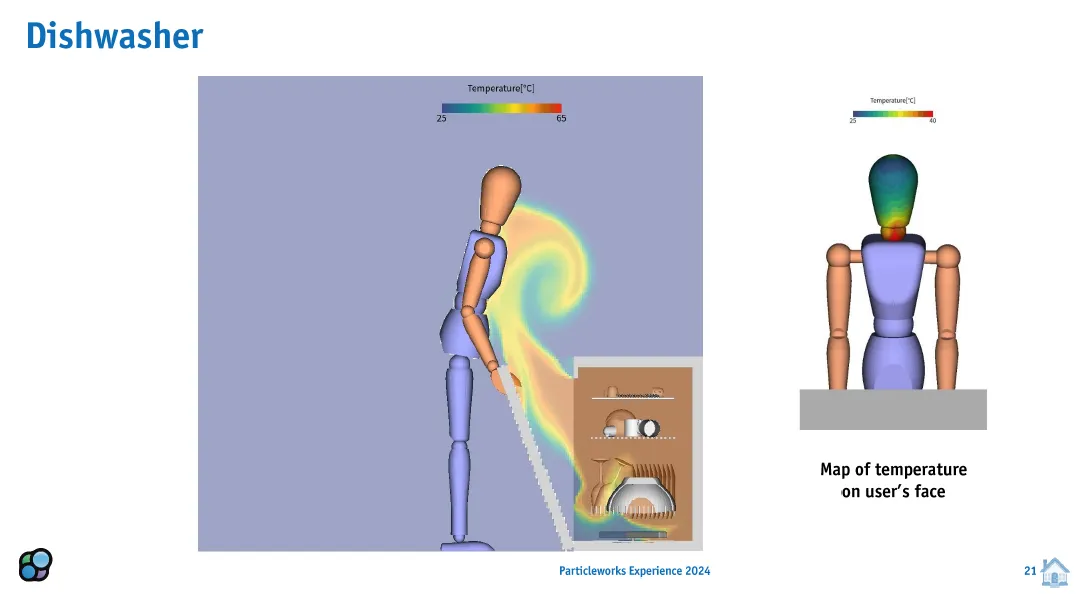
Enhanced Finite Volume Method (FVM) with Thermal Solver: Several improvements have been made to the FVM, which is used to simulate air, air-liquid coupling, and air-granule coupling. A key enhancement is the integration of a Thermal Solver, enabling the computation of temperature fields in air volumes. This addition facilitates the analysis of heat transfer between air and particles and assesses the influence of wall temperatures on the thermal field.
2. Multi-resolution Capabilities
Multi-Resolution (MR) for Enhanced Efficiency and Accuracy: Particleworks v8.1 introduces Multi-Resolution (MR) capabilities, allowing users to refine particle size and grid resolution in specific regions while maintaining coarser resolutions elsewhere. This approach balances accuracy and computational cost, making simulations more efficient.
Types of High-Resolution Regions: Users can define high-resolution regions in two ways: Box Region, which creates a rectangular box-shaped refined zone, or File (User-defined) Region, which uses an STL file to define a custom-shaped region for refinement.
Applying MR in Practical Applications: MR finds practical applications in various scenarios. Slide 61 in the sources demonstrates its use in improving airflow simulation in an e-motor, where a File MR Region accurately captures airflow near the windings, crucial for heat dissipation analysis.
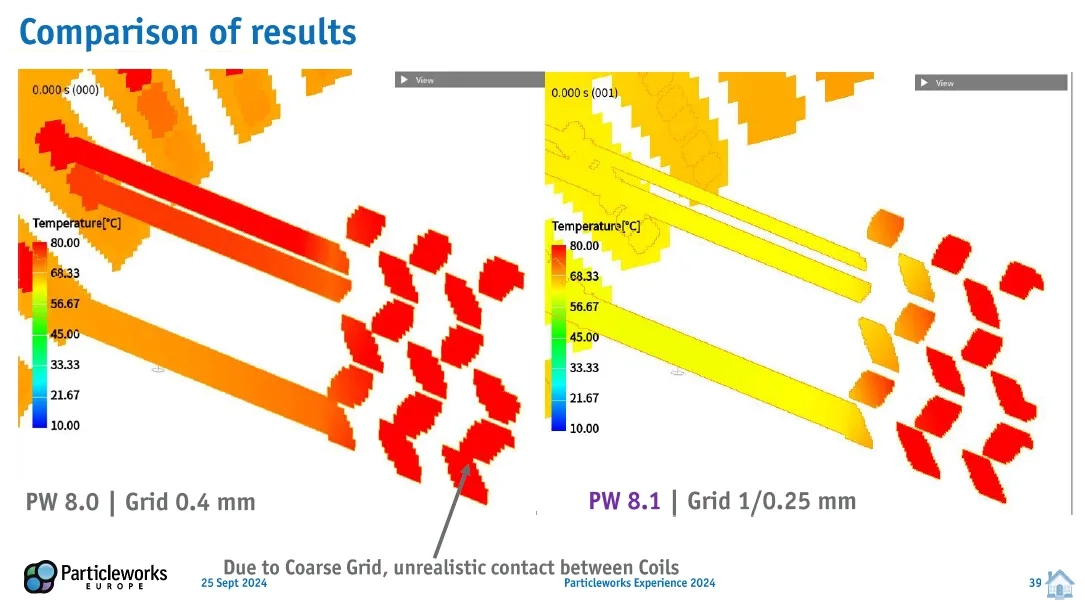
Custom Grid Interval for CHT Simulations: Particleworks v8.1 incorporates a custom Grid Interval feature, especially beneficial for Conjugate Heat Transfer (CHT) simulations. This feature allows users to define varying grid resolutions, leading to significant memory savings and reduced computation time without sacrificing accuracy. The sources demonstrate a tenfold reduction in memory usage compared to a uniform grid in v8.0.
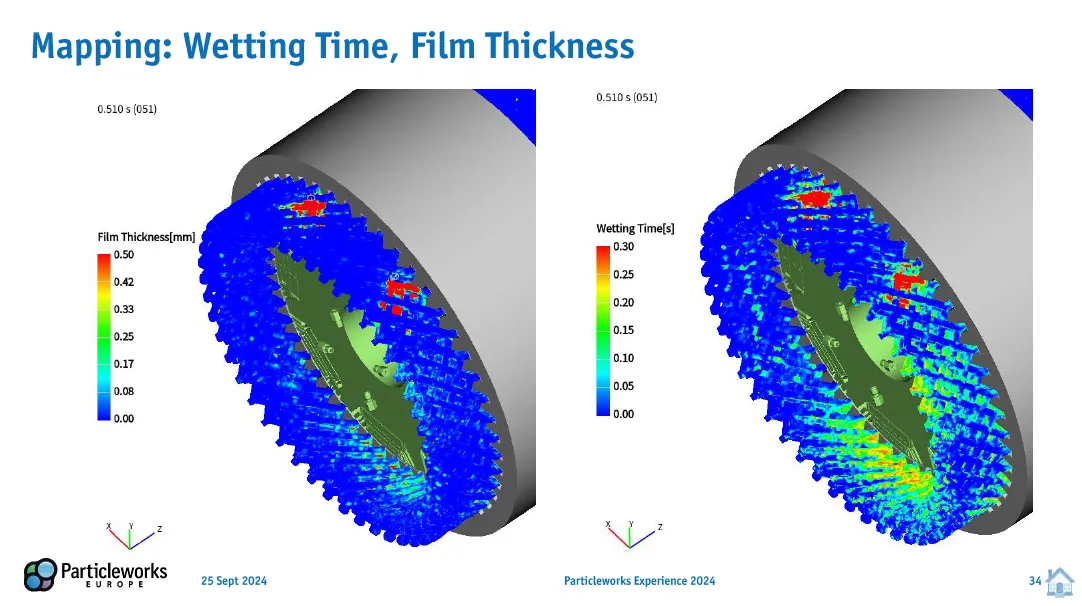
Enhanced Mapping Features for Deeper Analysis: Particleworks v8.1 introduces enhanced mapping features that provide comprehensive data analysis tools. Users can map wetting time and film thickness, modify default values for areas without fluid, and access a statistics.csv file containing information on average HTC, total map area, wetted area, and average wetting time. These features offer valuable insights into simulation results, facilitating informed design decisions.
3. Multi-Physics and GPU acceleration
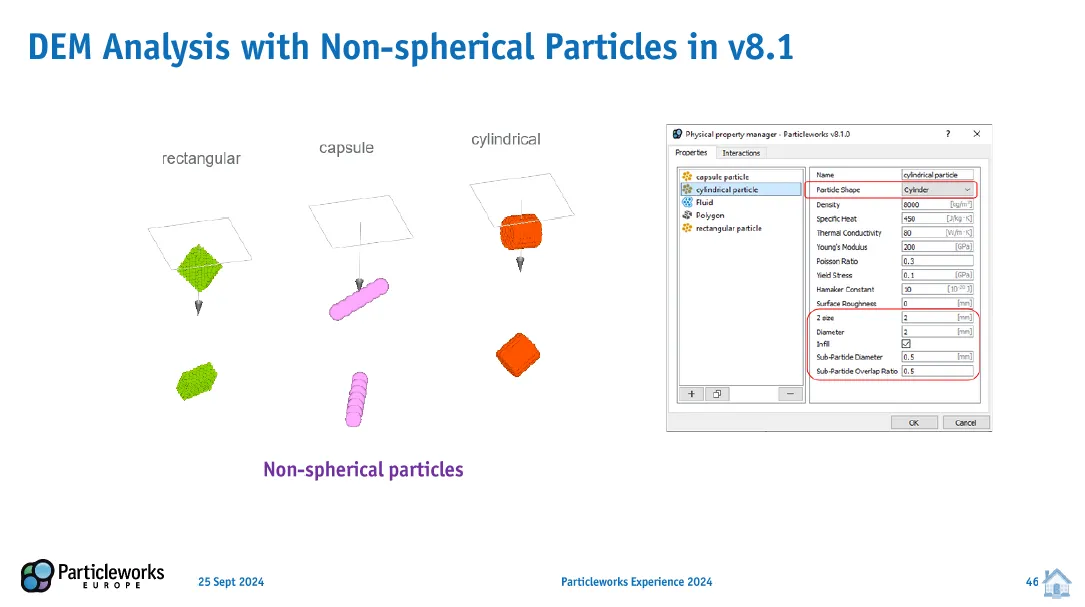
Non-Spherical Particle Analysis in Granuleworks: Granuleworks v3.1 introduces the ability to analyze non-spherical particles, capturing the anisotropic behavior of powders more realistically. This feature expands the simulation capabilities to scenarios involving non-spherical granular materials.
Excluded Volume Effect Model for High Granule Volume Fractions: A new Excluded Volume Effect Coupling Model is introduced for scenarios where granule volume is significant compared to fluid volume. This model ensures accurate representation of fluid displacement by granules, particularly in high-volume fraction scenarios.
Coarse Grain Model for Powder Simulations: For simulations involving powders with particle sizes too small for direct simulation, the Coarse Grain Model allows scaling up the powder size, making simulations more feasible.
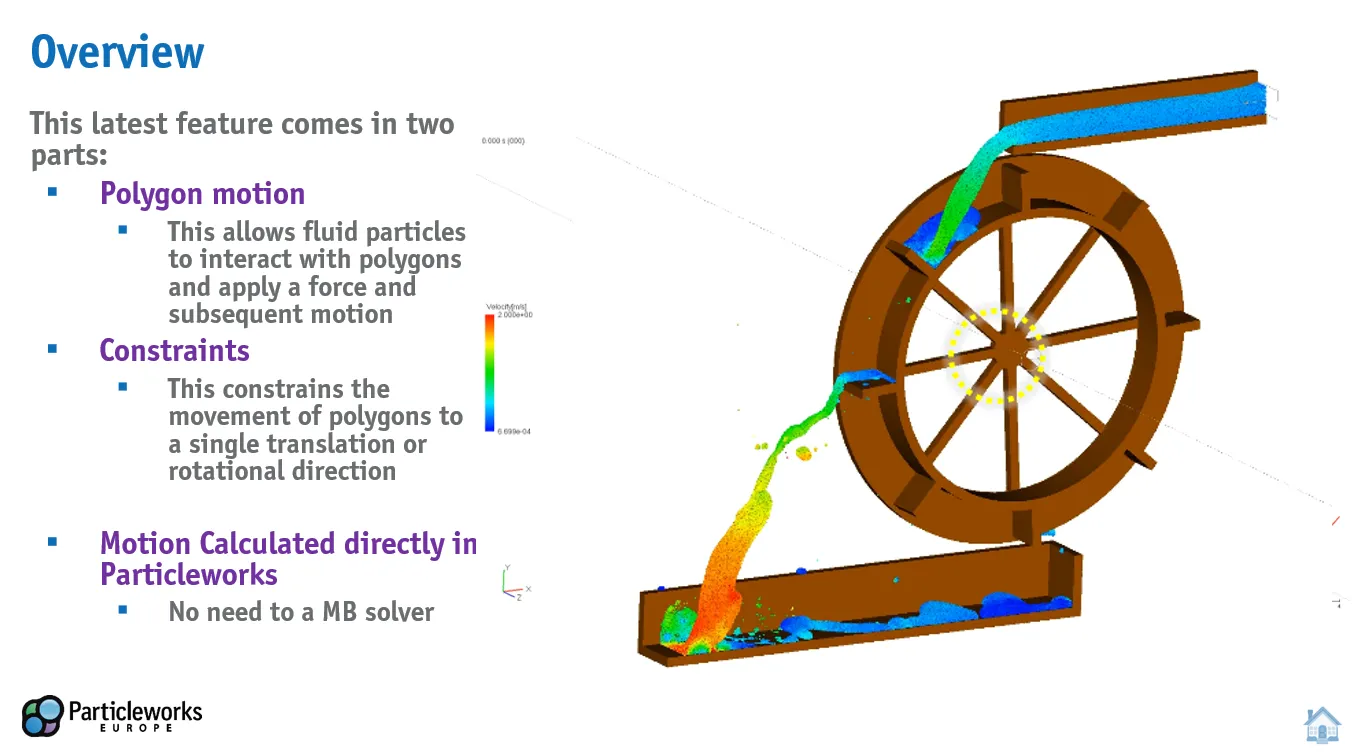
Rigid Body Motion with Constraints: Particleworks v8.1 enhances rigid body motion capabilities by enabling the simulation of 6-DOF motion for polygons influenced by forces from MPS particles. This feature supports DEM particles, FVM, and LBM, allowing users to simulate the motion of objects like flap gates and tanks.
GPU Computing and Scalability: Particleworks v8.1 leverages the power of GPU computing for faster and more efficient simulations. Benchmarking results presented in the sources demonstrate the significant performance improvements achieved with various GPUs compared to a CPU baseline. The scalability of multi-GPU setups further enhances performance, allowing for the simulation of larger and more complex models.
Particleworks blog
Enjoy our latest blog articles!
We will go over some of the simulation practices from the mesh-less solver and from the intuitive interface, that make the simulation process simple and fast.
Glossary
Take a look at the glossary dedicated to the terms of Moving Particle Simulation.